Free Shipping on Orders over $99 for Whole USA

What’s the difference between single-mode and multi-mode fiber SFP transceivers?
What’s the Difference between Single-Mode and Multi-Mode Fiber SFP Transceivers?
As fiber optic technology keeps advancing, choosing the right components is critical for optimizing network performance and efficiency. One such component that plays a pivotal role in ensuring smooth data transmission is the SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) transceiver. For those in the fiber optic communication industry, understanding the difference between single-mode and multi-mode fiber SFP transceivers is crucial for making smart purchasing decisions.
What is an SFP Transceiver?
Before diving into the differences between single-mode and multi-mode, let’s briefly cover what an SFP transceiver is. SFP optical transceivers are compact, hot-pluggable devices that enable the transmission and reception of data over optical fiber or copper cables. These optical modules are essential in modern networking systems, providing flexibility and scalability in applications ranging from enterprise networks to data centers.
Single-Mode Fiber SFP Transceivers
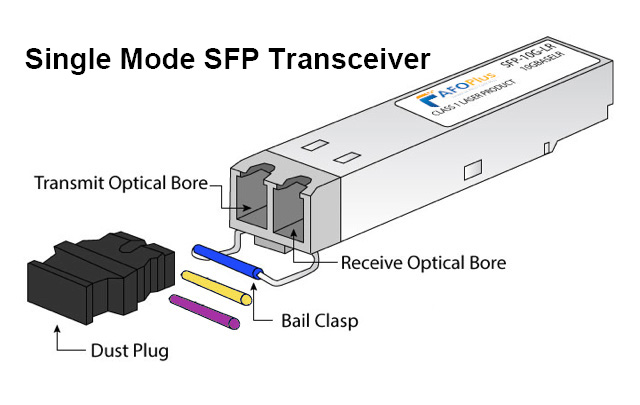
Single-mode fiber SFP optical transceivers are designed for long-distance communication, utilizing thin glass fibers that allow optic to travel in a straight line. The key feature of single-mode fiber is that it supports higher bandwidths over greater distances compared to multi-mode fibers. Single-mode transceiver modules typically operate at higher speeds (up to 100Gbps and beyond) and are ideal for connections over several kilometers, with some models capable of spans of up to 80 kilometers or more.
These optical modules typically use a laser light source (such as a distributed feedback laser, or DFB laser) to emit a narrow, coherent beam of light, ensuring that the signal maintains integrity over long distances. Single-mode fiber SFP transceivers are common in metropolitan area networks (MANs), long-haul communications lines, and high-performance data centers, where low attenuation and high-speed transmission are required.
Multi-Mode Fiber SFP Transceivers
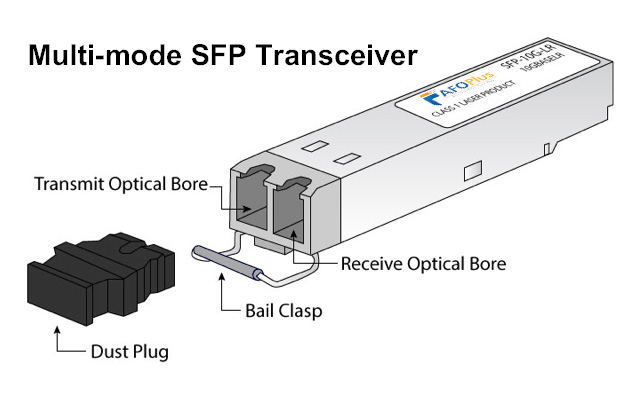
On the other hand, multi-mode fiber SFP modules are used for shorter distances, typically within a building or campus. Multi-mode fibers have a larger core diameter, allowing multiple optic modes to travel simultaneously. As a result, multi-mode fiber transceivers are more affordable than single-mode solutions, though they have limitations when it comes to distance and bandwidth.
Multi-mode fiber SFP transceivers commonly operate with LED or VCSEL (Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser) light sources, which are less expensive than the laser sources used in single-mode fiber transceivers. However, the signal quality degrades faster over longer distances due to modal dispersion, which is why multi-mode fiber is generally limited to shorter-range applications. Typical distances range from 300m to 2km, depending on the type of multi-mode fiber and the specific transceiver model.
Key Differences Between Single-Mode and Multi-Mode Fiber SFP Transceivers

Distance and Bandwidth:
Single-mode fiber SFP modules excel in long-distance data transmission, providing significantly higher bandwidth over distances of up to 80km or more.
Multi-mode fiber SFP transceivers are better suited for shorter distances (up to 2km), with lower bandwidth capabilities compared to single-mode options.
Cost Considerations::
Single-mode fiber SFP optical transceivers are generally more expensive due to the advanced technology required for long-distance transmission, such as laser light sources and precision optics.
Multi-mode fiber SFP transceivers are more affordable, making them a cost-effective solution for applications within buildings or short-range networks.
Transmission Speed:
Single-mode fiber supports higher transmission speeds, including 10Gbps, 40Gbps, and 100Gbps, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
Multi-mode fiber typically operates at speeds of 1Gbps to 10Gbps, making it suitable for lower-speed applications within shorter distances.
Wavelength of SFP Transceiver
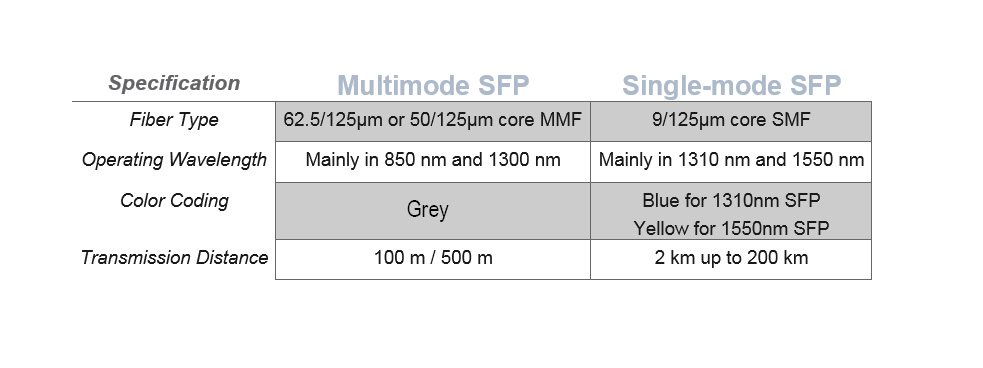
Single-mode SFP module has a narrower laser wavelength, which works essentially in 1310nm and 1550nm wavelength.
However, the multi-mode SFP module works in 850nm wavelength because of the bigger core size.
Which Fiber SFP Transceiver Should You Choose?
The choice between single-mode and multi-mode fiber SFP optical transceivers depends largely on the requirements of your network. If you’re building a long-distance network, such as a data center interconnect or a metropolitan area network, single-mode fiber SFP modules are the clear choice due to their superior performance over long distances. However, for local area networks (LANs) or in-building installations where cost-effectiveness is a priority, multi-mode fiber SFP module offer a more practical solution.
Conclusion
Both single-mode and multi-mode fiber SFP transceivers have distinct advantages depending on the specific needs of the network. Single-mode fiber transceivers provide excellent performance over long distances, while multi-mode fiber transceivers offer a more affordable option for shorter-range applications. By carefully considering the scope of your network and the distance between components, you can make an informed decision that balances cost, performance, and future scalability.
To ensure the highest quality and reliability in your fiber optic components, consider visiting our online store www.afoplus.com
for a wide selection of SFP modules that meet the demands of the modern communication industry.
